What is Gingival Hyperplasia?
Gingival Hyperplasia is a diagnosis based on histopathology (i.e. a pathologist reviews the sample under the microscope to make this diagnosis). Gingival enlargement is the diagnosis based on clinical observation prior to histopathology. This condition can be a result of genetic predisposition, trauma to the gum tissue, or caused as a side effect of certain drugs. Gingival enlargement creates pseudo-pockets (i.e. false pockets) between the gingiva and the teeth allowing plaque, calculus, and debris to accumulate which leads to periodontal disease. Treatment requires cutting the enlarged gum tissue back to near normal, a procedure called gingivectomy/gingivoplasty. This is performed using scalpel blades as well as the use of laser/cautery along with diamond burs. Typically, samples of the removed tissue are sent to the lab for evaluation by a pathologist. This condition can reoccur, however, meticulous home care combined with regular professional cleanings are recommended to control plaque and delay reoccurrence.
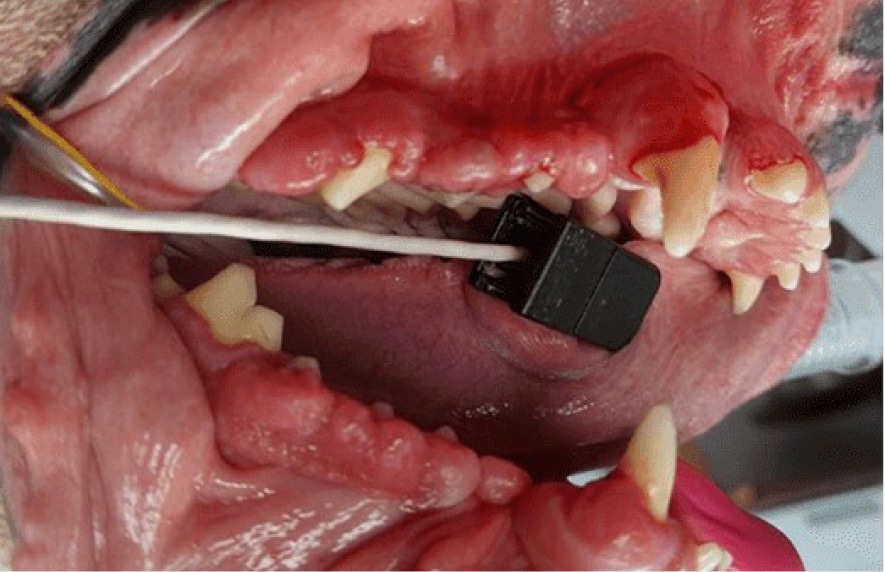
Before
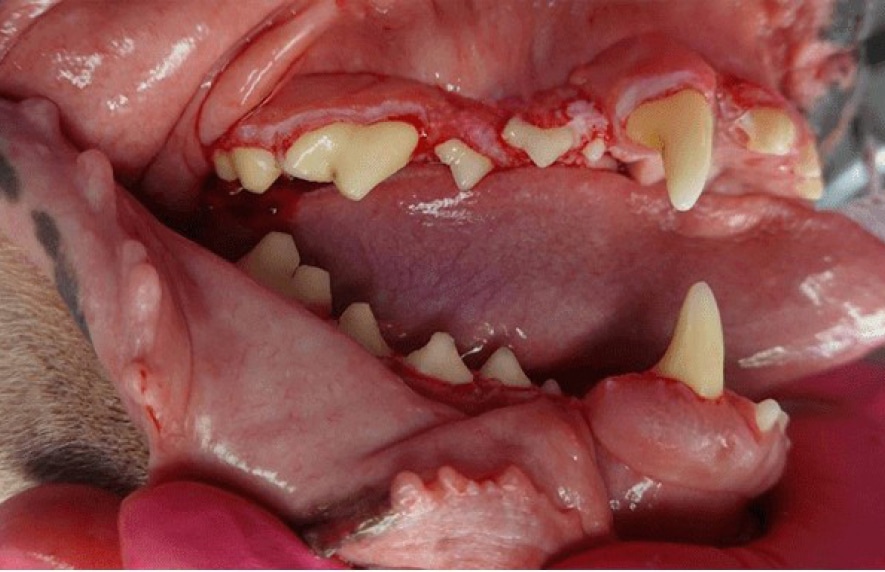
After
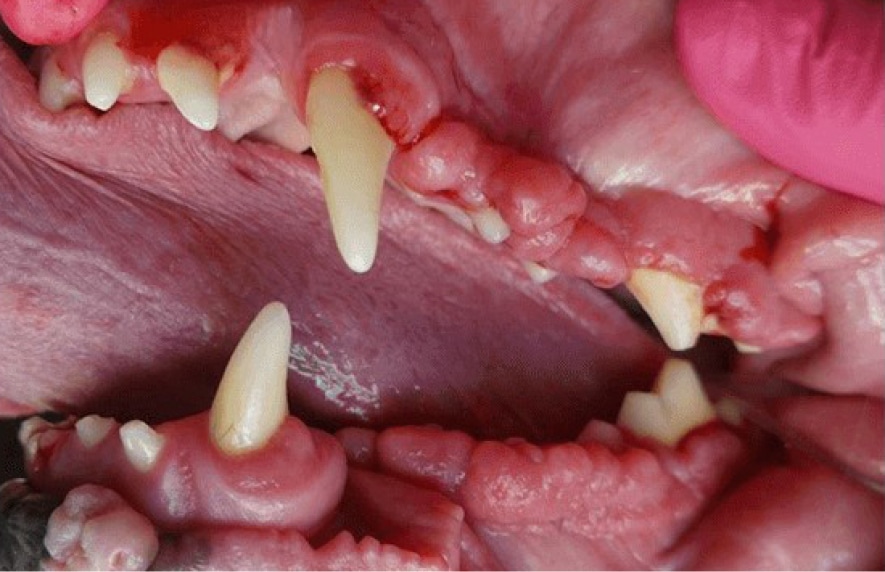
Before
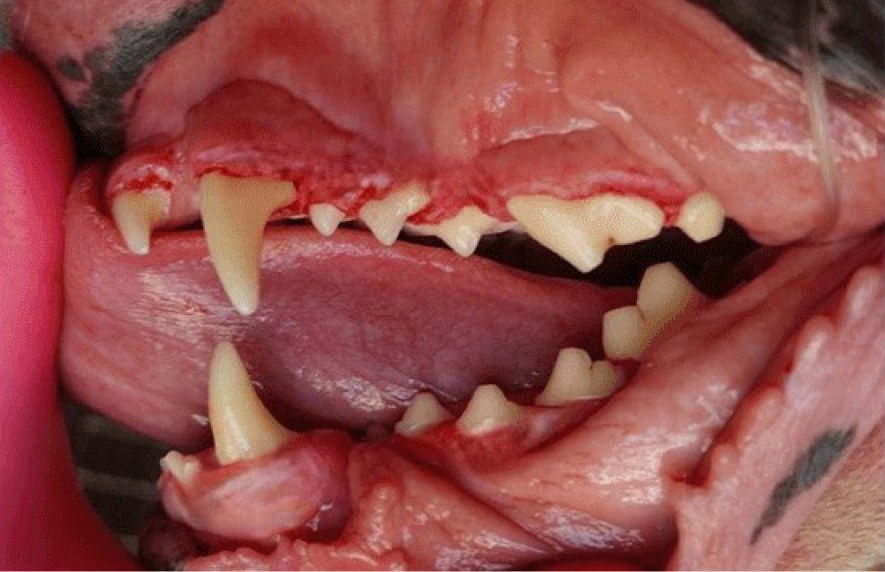
After
Headline Here
This is just placeholder text. Don’t be alarmed, this is just here to fill up space since your finalized copy isn’t ready yet. Once we have your content finalized, we’ll replace this placeholder text with your real content.
Sometimes it’s nice to put in text just to get an idea of how text will fill in a space on your website.
Traditionally our industry has used Lorem Ipsum, which is placeholder text written in Latin. Unfortunately, not everyone is familiar with Lorem Ipsum and that can lead to confusion. I can’t tell you how many times clients have asked me why their website is in another language!

Call (218) 461-4825 or book online to schedule your pet’s advanced dental appointment.
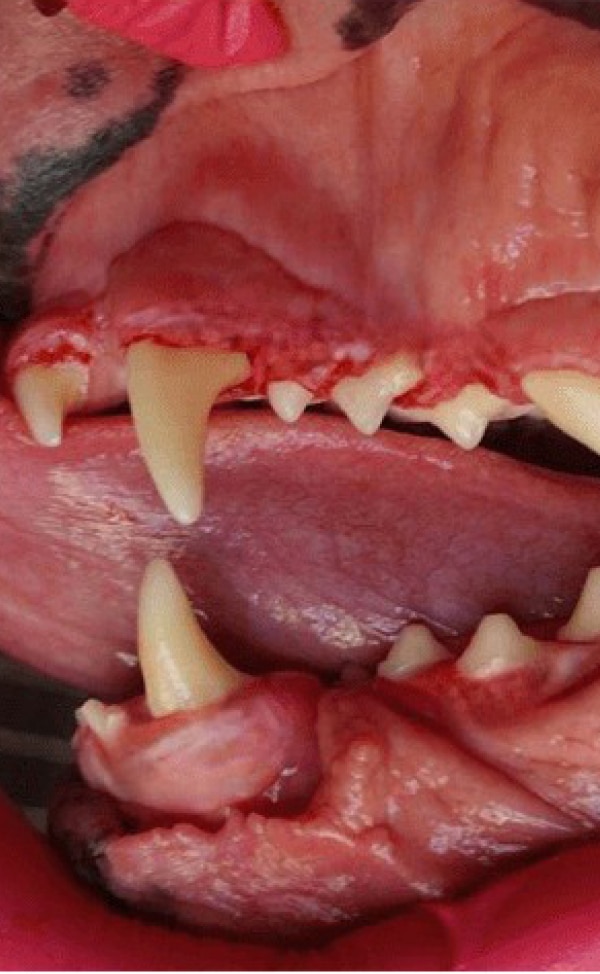
Frequently Asked Questions About Treating Gingival Enlargement in Dogs and Cats
How is gingival hyperplasia treated, and can it reoccur?
Treatment for gingival hyperplasia involves a gingivectomy or gingivoplasty, where the enlarged gum tissue is surgically removed using scalpels, lasers, or other tools. Although the condition can reoccur, consistent home care and regular professional dental cleanings help control plaque and reduce the likelihood of reoccurrence.
Why is gingival enlargement a concern for pets?
Gingival enlargement creates pseudo-pockets between the gums and teeth, where plaque, calculus, and debris can accumulate. This buildup can lead to periodontal disease, making early detection and treatment crucial for maintaining your pet’s oral health.

