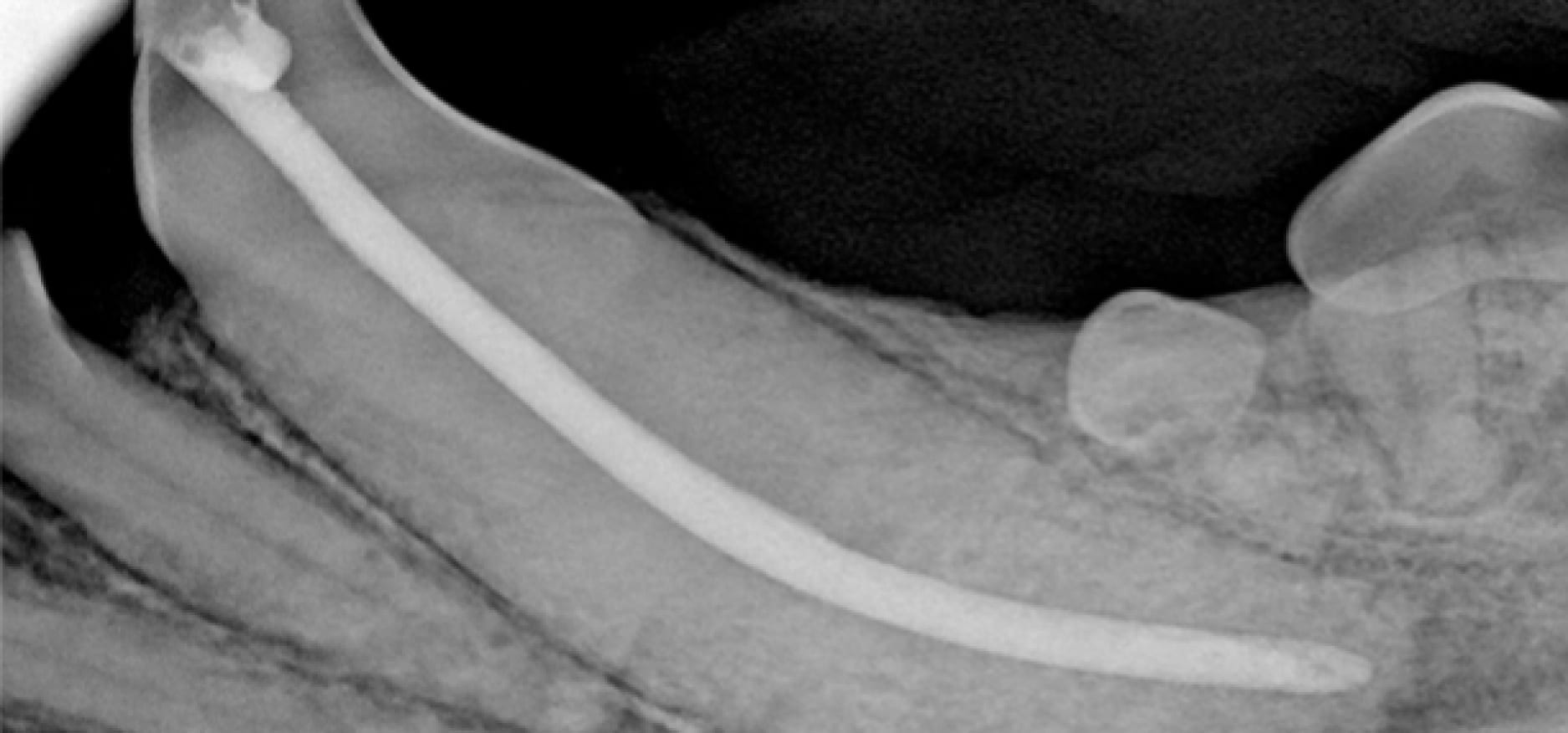
Jaw Fractures & Oral Trauma
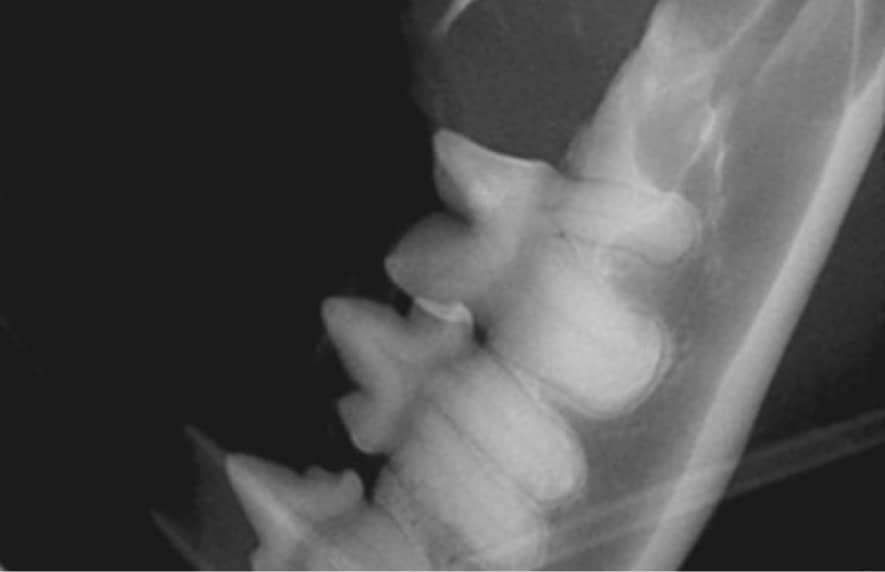
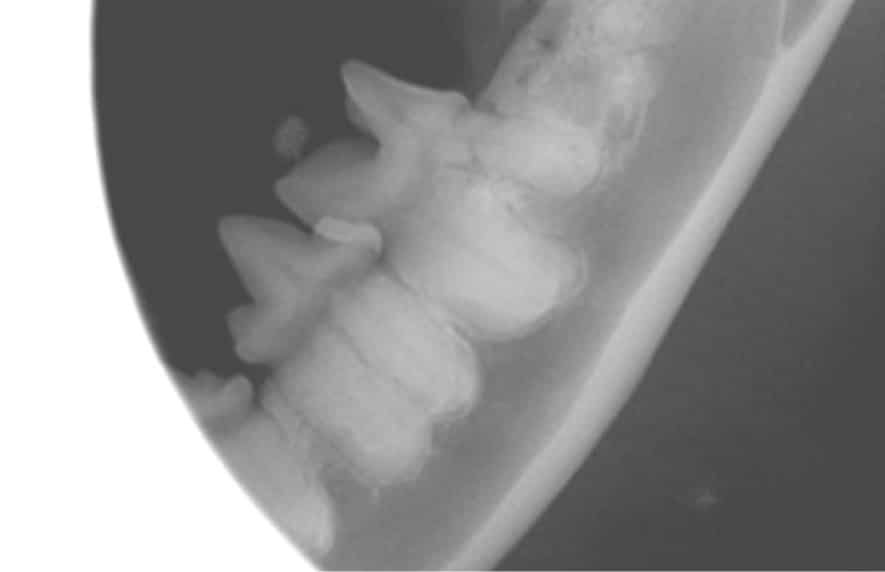
Jaw fractures are typically seen in pets with trauma (such as being hit by a car, animal bites, or in relation to periodontal disease). We will perform a thorough workup of your pet’s issues including full mouth dental radiographs to assess the dentition and location of the fracture.

Treatment and Healing Time
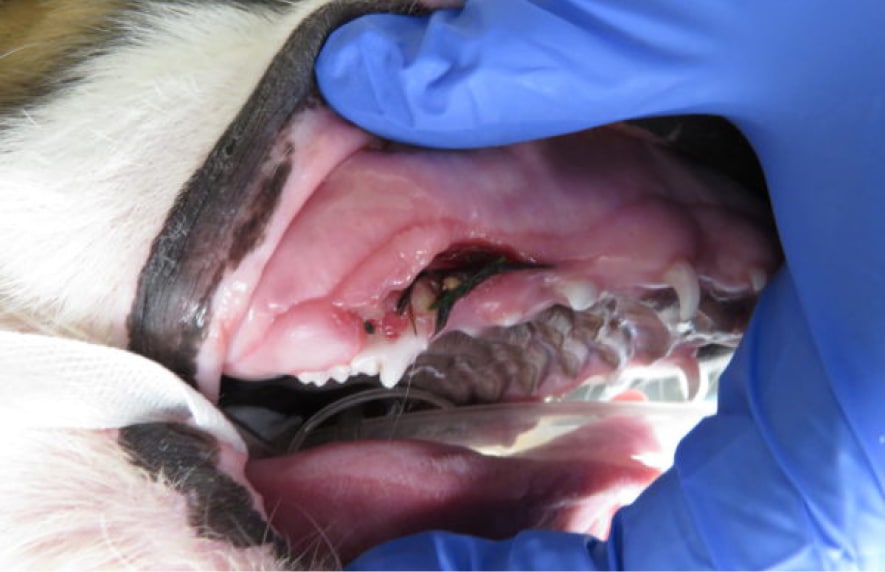
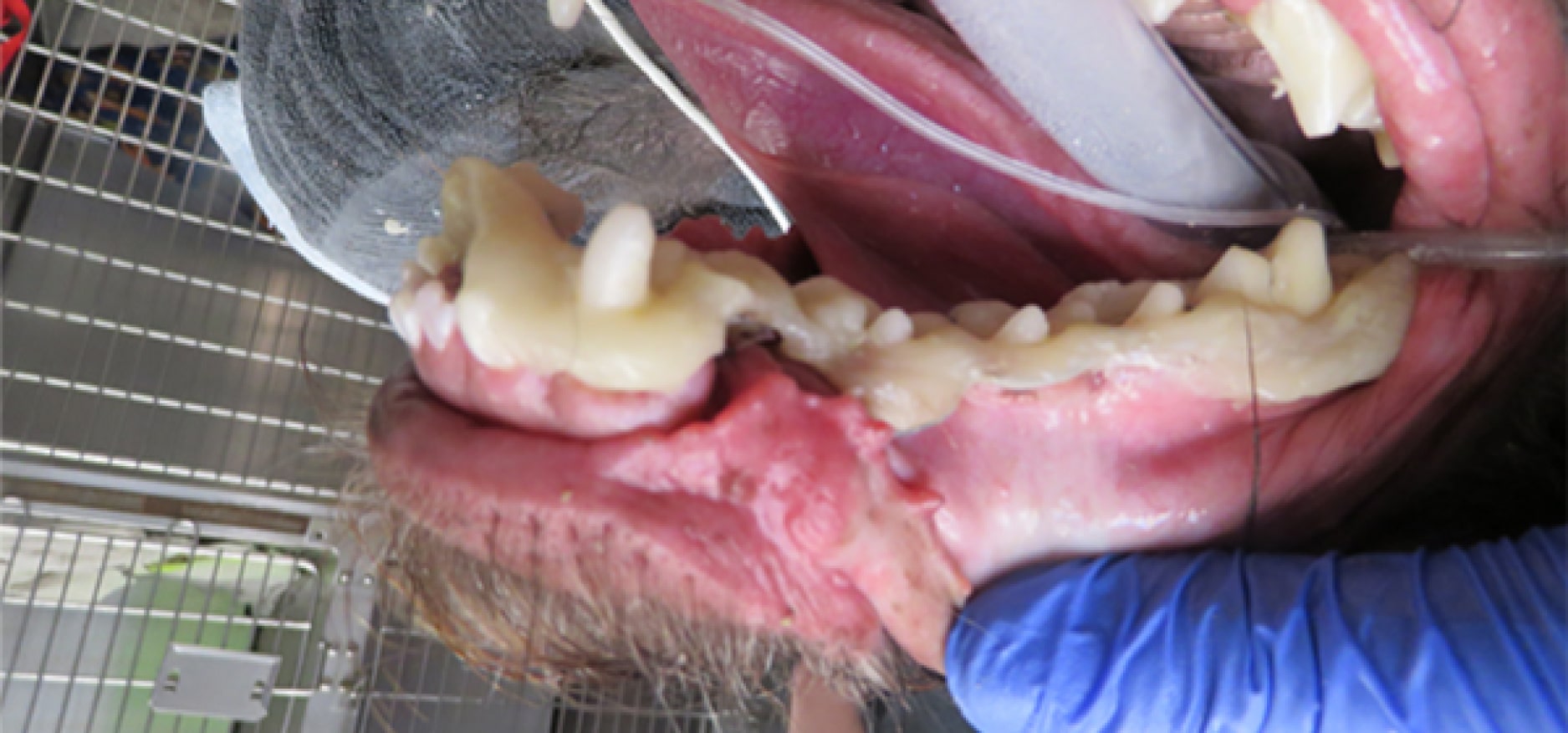
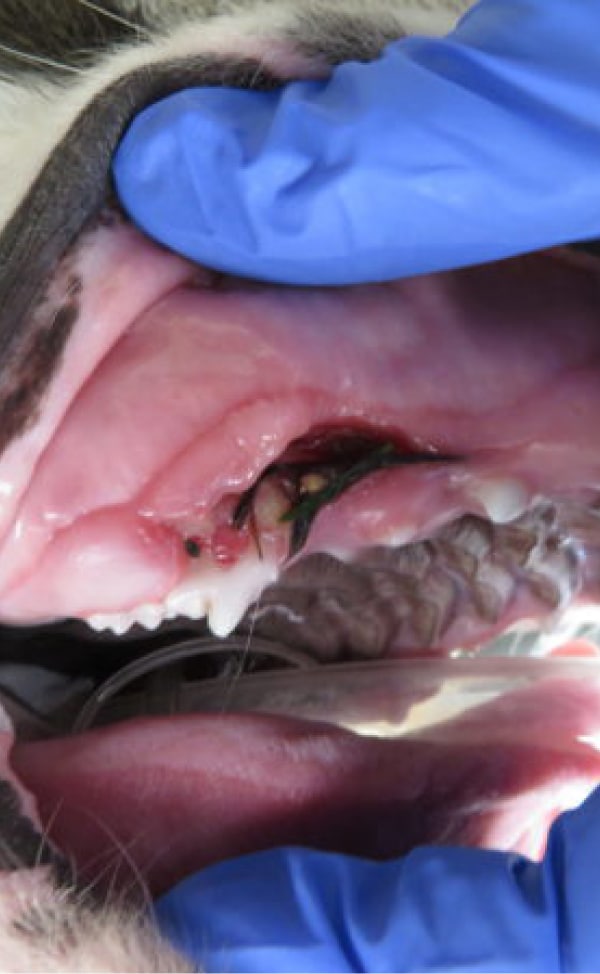
Treatments may include interosseous wire (wire placed into the bone to allow for appropriate jaw alignment), intradental splint (wiring and acrylic material) or various other techniques to assist in your pet’s healing. Any wire or splints which aid in immobilizing the fracture site will require surgical removal after the fracture has healed.
The healing time may vary depending on the age of the patient as well as the severity of the fracture. Typically healing time occurs within 4 to 8 weeks. Older dogs may require a longer length of placement for splints/wire than younger dogs. Typically at a 2-week recheck, we will determine to follow-up care and when to remove the appliance (if one was used).
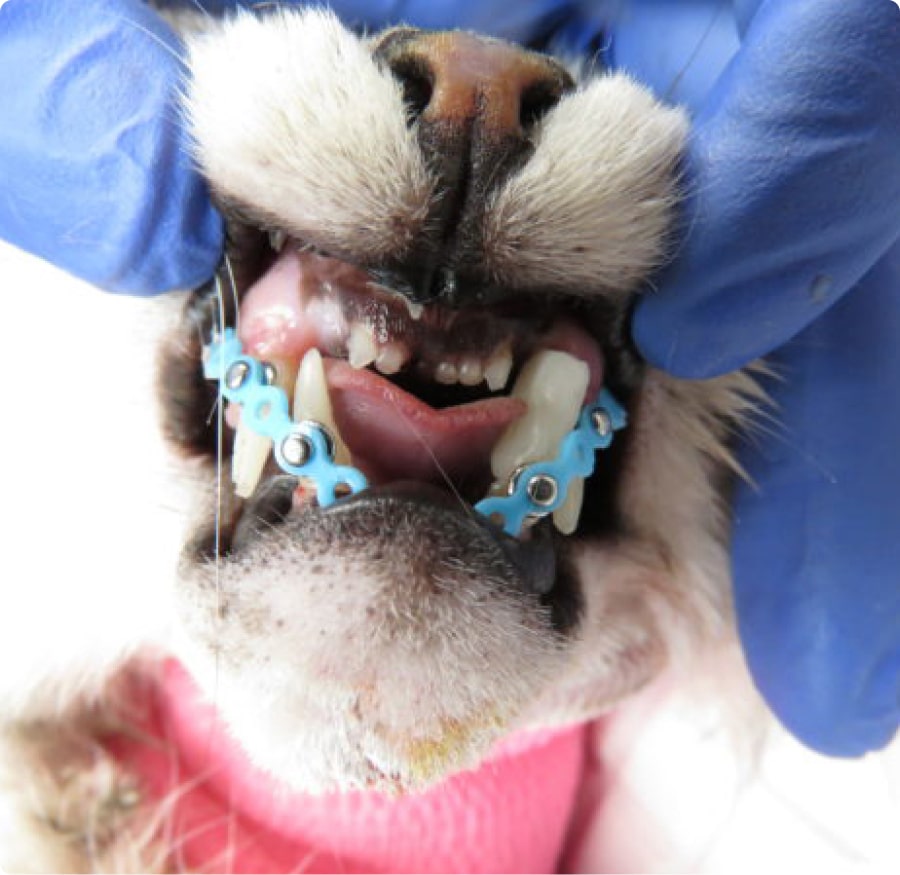
Severe Jaw Fractures and TMJ Luxation
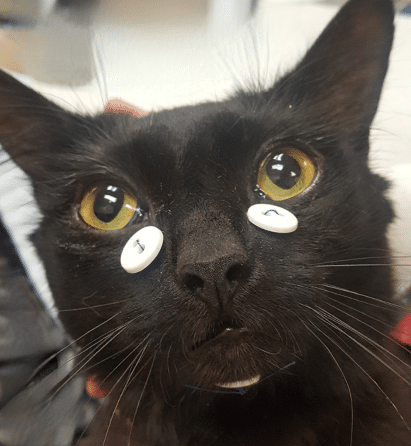
In severe jaw fractures or temporomandibular joint luxations (TMJ luxation) placement of an appliance to reduce motion is often necessary to allow for healing. This can be accomplished with a soft muzzle, maxillary mandibular fracture fixation devices or usage of buttons (such as the labial button technique). These options will be provided based on the pet’s type of fracture or luxation and available techniques to promote appropriate healing. The goal of any treatment is a comfortable occlusion and a mouth free of pain and infection.
Before
After
Before
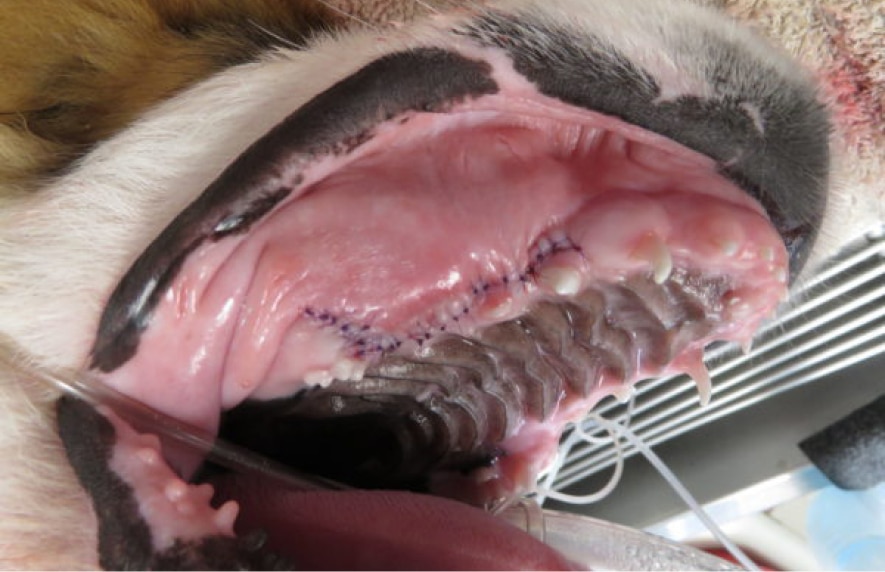
After
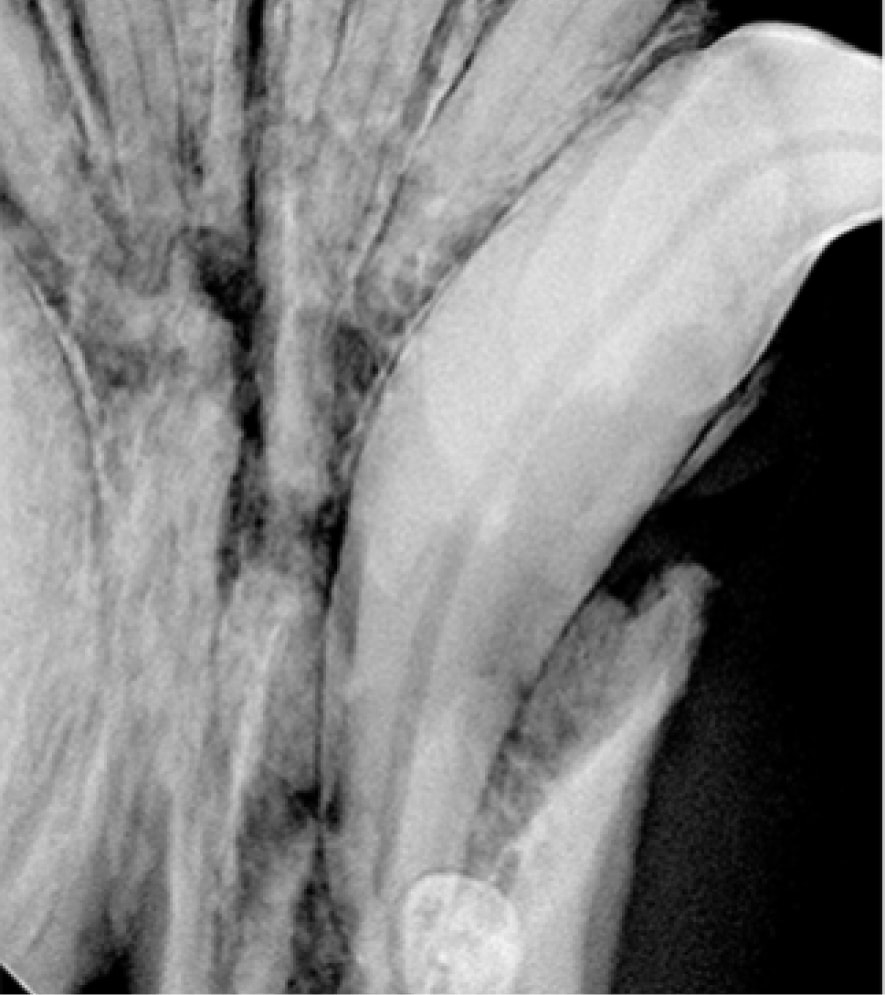
Before
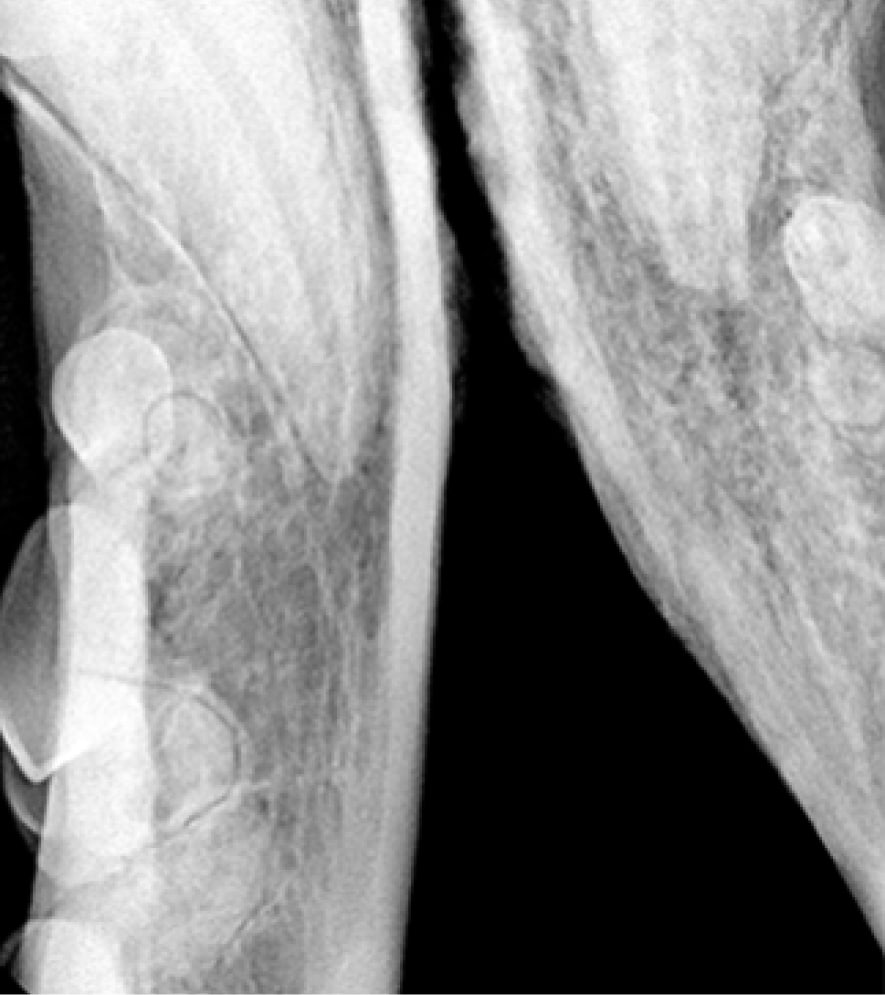
After

Headline Here
This is just placeholder text. Don’t be alarmed, this is just here to fill up space since your finalized copy isn’t ready yet. Once we have your content finalized, we’ll replace this placeholder text with your real content.
Sometimes it’s nice to put in text just to get an idea of how text will fill in a space on your website.
Traditionally our industry has used Lorem Ipsum, which is placeholder text written in Latin. Unfortunately, not everyone is familiar with Lorem Ipsum and that can lead to confusion. I can’t tell you how many times clients have asked me why their website is in another language!

Call (218) 461-4825 or book online to schedule your pet’s advanced dental appointment.
Frequently Asked Questions About Jaw Fractures & Oral Trauma
What are the treatment options for severe jaw fractures or TMJ luxation in pets?
In cases of severe jaw fractures or temporomandibular joint (TMJ) luxation, treatments may involve appliances to limit jaw movement, such as soft muzzles, fracture fixation devices, or the labial button technique. These options are tailored to each pet’s needs to ensure a pain-free, comfortable recovery and proper occlusion.
How are jaw fractures treated in pets, and what is the healing time?
Jaw fractures in pets are treated using techniques like interosseous wires, intradental splints, or other immobilization methods to allow proper alignment and healing. Healing time can vary between 4 to 8 weeks, depending on the severity of the fracture and the pet’s age, with older pets often requiring longer recovery periods.
What causes jaw fractures in pets, and how are they diagnosed?
Jaw fractures in pets are typically caused by trauma, such as car accidents, fights with other animals, or severe periodontal disease. To diagnose the extent of the injury, a thorough workup, including full-mouth dental radiographs, is performed to assess the fracture location and overall oral health.
