Advanced Oral Surgery
Pets can be affected by a variety of oral conditions which may require a dog or cat to have surgery. Here at Minnesota Veterinary Dental Specialists, our specialist is well equipped to perform a wide assortment of veterinary oral surgeries. These include preserving teeth, removing harmful growths, repairing injuries, correcting jaw fractures, removing large oral tumors and much more. Improving your pet’s oral health and overall quality of life is our top priority. We will ensure you are part of every step of the process to ensure the best outcome for your furry family member.
- This is just a placeholder headline, we will replace it once your website copy is finalized.
- While often hilarious, these placeholder passages can also lead to much of the same confusion.
- If you’re curious, this is Website Ipsum. It was specifically developed for the use on development websites.
- Other than being less confusing than other Ipsum’s, Website Ipsum is also formatted in patterns more similar to how real copy is formatted on the web today.
Conditions Treated with Oral surgery
Extractions of diseased dentition due to periodontal disease
Tooth Extractions
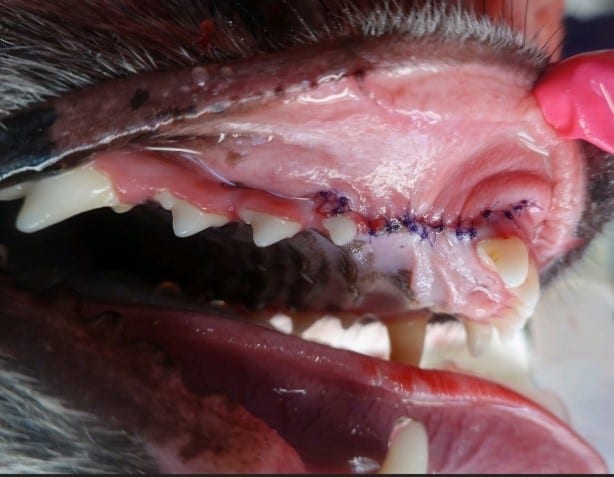
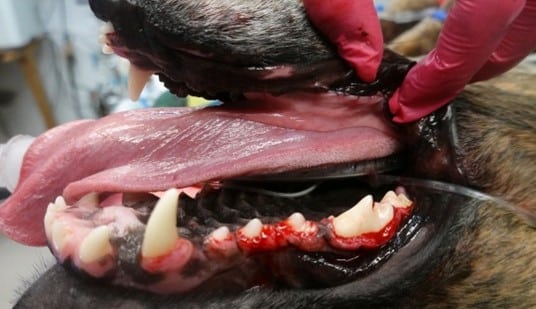
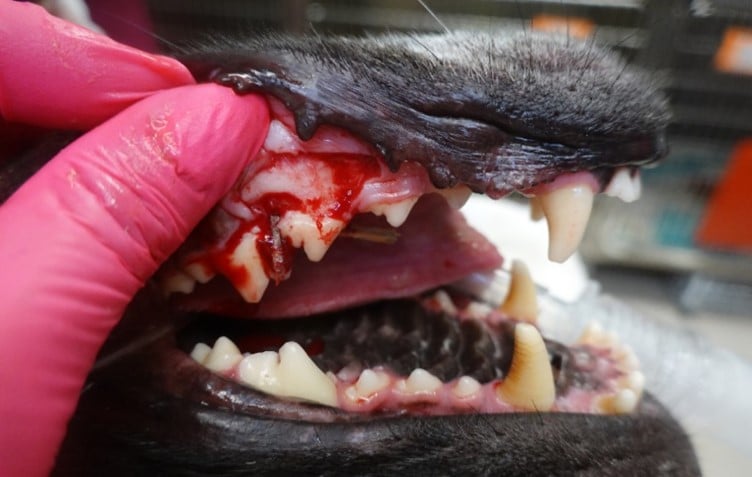
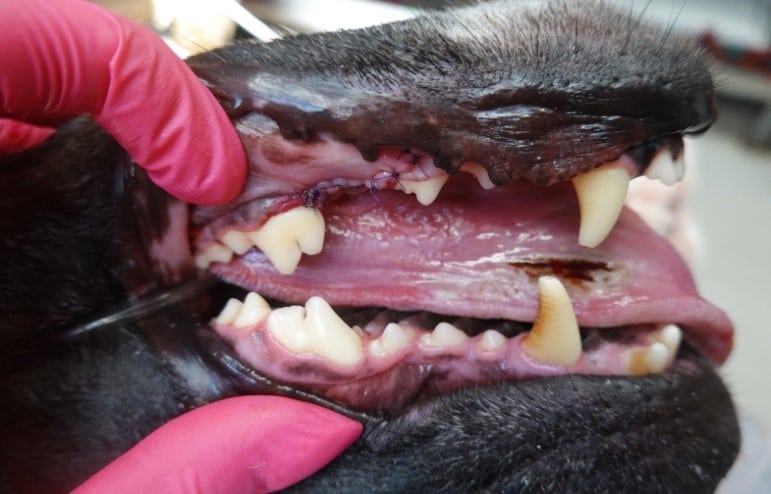
Most tooth extractions require an incision of the gingiva and minimal removal of bone to ensure extraction of the entire tooth. Some teeth require tooth sectioning to ensure full root removal. Care should be taken especially when extracting mandibular canines and first molars, as improper technique can lead to jaw fractures. Surgical extraction sites are sutured closed to prevent complications during the healing process. The sutures dissolve on their own in 2-8 weeks.
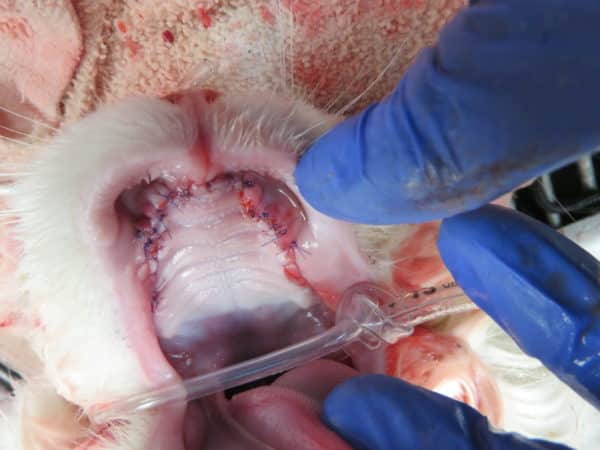
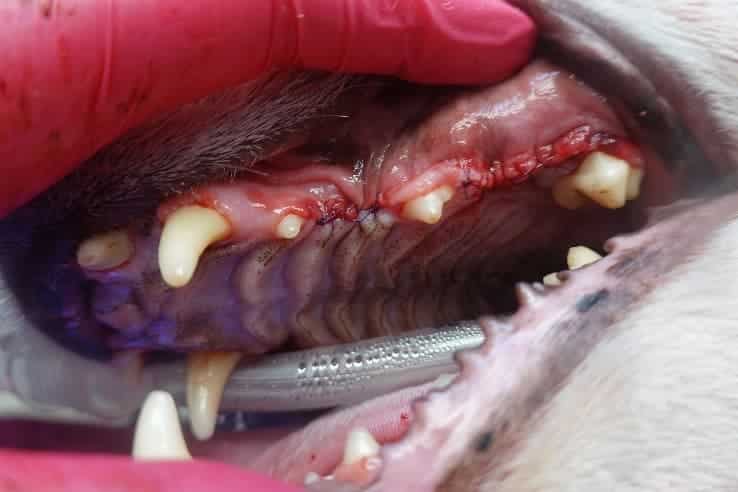
Jaw Fractures
This is when trauma occurs to one or multiple portions of the jaw which requires treatment.
-
- Less invasive options that may be recommended:
- Tape muzzle
- Labial button technique
- More invasive options that may be recommended:
- Interdental wiring with composite splint
- Interosseous wiring
- Maxillary mandibular fixation device
- Plating
- Options are based on the type of fracture and creating the best outcome for your pet.
- Less invasive options that may be recommended:
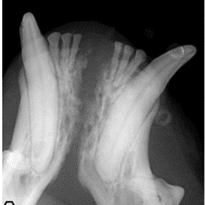
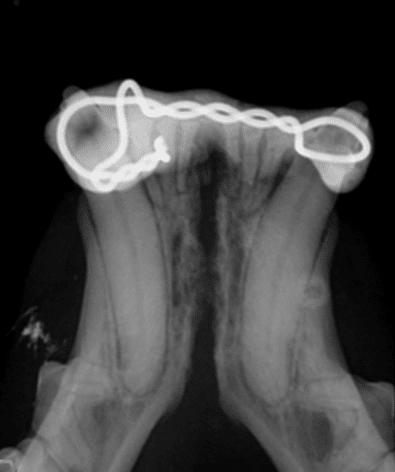
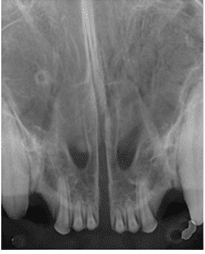
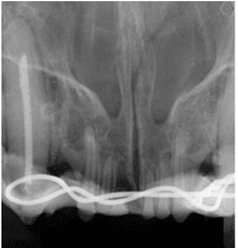
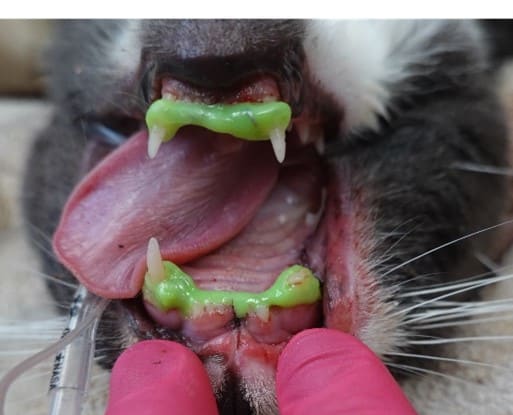
Fractured teeth
While we often try to save fractured teeth, when possible, with root canal therapy, this is sometimes not an option for damaged teeth (especially if the damage goes below the gumline).
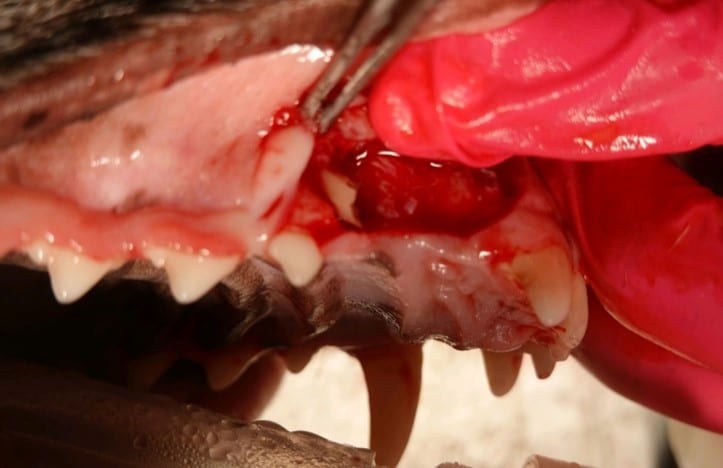
Oral Masses
No oral mass in the mouth should be ignored. It is important to determine if the tumor is benign or malignant. Even benign tumors can become very aggressive and require large oral surgery.
-
- Types of procedures offered:
- Incisional biopsy
- Excisional biopsy
- Maxillectomy
- Mandibulectomy
- rim
- Segmental
- Near subtotal
- The goal of oral tumor removal is clean surgical margins for best outcome surgically for your pet.
- Types of procedures offered:
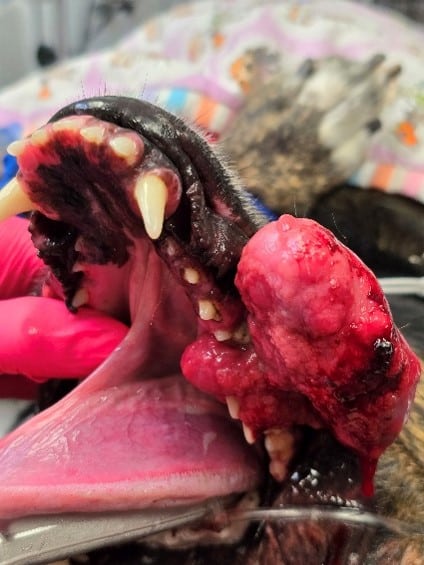
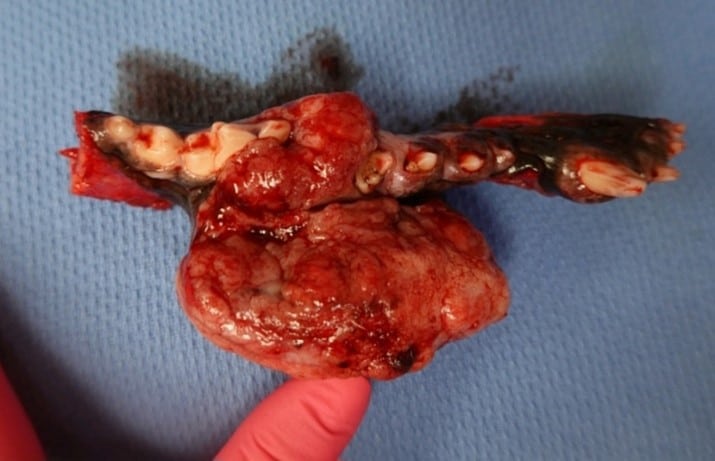
Oral Cyst Removal
Surgical Procedures
Our specialist utilizes the most advanced veterinary dental technology and techniques to perform surgical procedures. Other procedures which may require surgery include:
Extractions of diseased dentition due to periodontal disease
Oral Foreign Body Removal
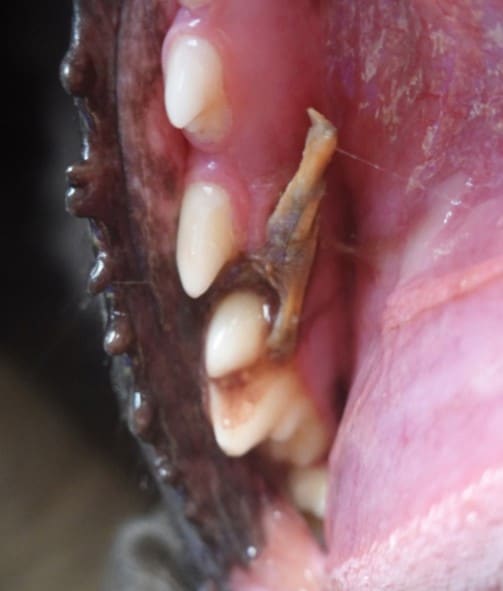
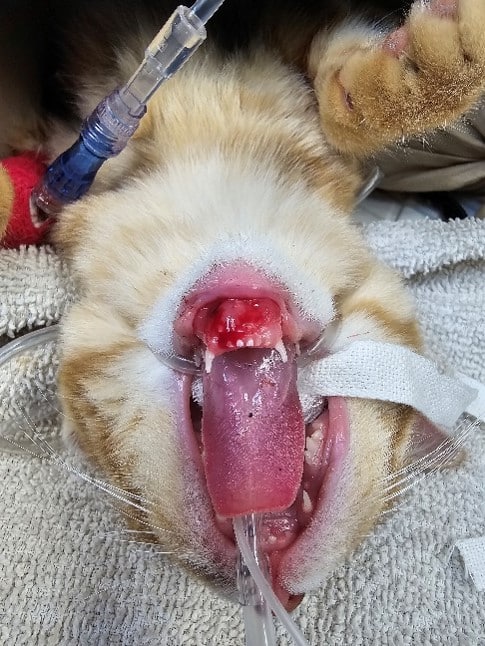
Palatal Defect Repair
Mandibular Lip Avulsion

Call (218) 461-4825 or book online to schedule your pet’s advanced dental appointment.
Frequently Asked Questions About Advanced Oral Surgery
What should I expect for my pet after oral surgery?
- Your pet may have mild oral discharge for 3-5 days dependent on the type of oral surgery performed
- Sutures that are placed within the mouth are dissolvable and will normally dissolve within 2 to 3 weeks.
- Your pet will need to be on a wet diet or softened diet for 10-14 days
- An endotracheal tube is always placed during surgery to deliver gas anesthetic agents, protect the airway from fluid and bacteria, and to allow us to control breathing if needed. The ET tube may cause tracheal irritation, and a cough is not unusual for 1-2 days after intubation. Please call if coughing is severe or does not resolve in 2-3 days.
What types of complications may occur after oral surgery?
Although rare, postoperative complications can include the following:
- Swelling
- Severe bleeding
- Infection
- Dehiscence (opening of the surgical sites).
- Anesthetic agents can cause short-term dysphoria, disorientation, whining or howling, incoordination, loss of control of bladder or bowels.

